Techlion Display
LCD Module Manufacturer
The Development Status & Trend of Global OLED Industry
In the 21st century, people need a new generation of flat-panel displays with better performance, more in line with the future needs of life, in order to meet the so-called “4Cs”, namely, computers (com pute r), communications (comm unication), consumer electronics (cons ume r electronics), The 4Cs are computers, communications, consumer electronics, automotive electronics, and the 3G era. In particular, the future trend is to. In particular, the future trend is to deliver a large amount of information and images on a lightweight and flexible body, and today’s flat panel displays no longer meet the demand.
After CRT, LCD, PDP technology, display technology is moving towards large area, ultra-thin, low cost, flexible, etc. OLED is in line with the future development direction of flat panel display technology due to its many advantages. OLED is in line with the future development direction of flat panel display technology because of its many advantages. The development history of display technology is shown in Figure 1. Therefore, some experts say that the most promising industry in the 21st century is “OLED”, which is called “dream display”.
Contents
1 OLED Overview
OLED industry chain composition
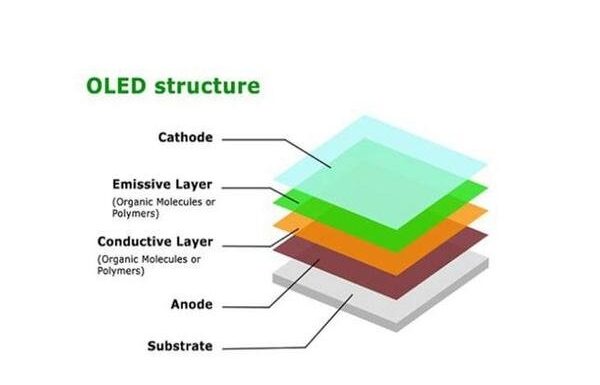
According to the technical principle and preparation process of OLED, the OLED industrial chain is usually divided into four main parts: equipment supply, material supply, driver module development and supply, panel and device supply and downstream users, as shown in Figure 2.
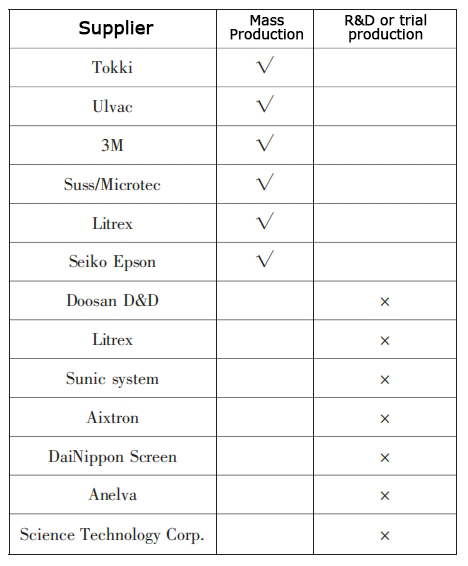
The global OLED major equipment manufacturers are Tokki, ULVAC, Aixtron, Litre x, OTB, MicroFab, DooSan, Seiko Eps on, Sunic, etc. Table 1 shows the suppliers of mass-production and R&D/pilot-production OLED vaporization equipment. At present, there are only a few domestic manufacturers conducting research and development of OLED production equipment.
According to iSuppli, Japanese equipment suppliers have taken an early lead in the OLED manufacturing equipment market by capitalizing on their strengths in semiconductor and LCD manufacturing. tokki Corp. and Ulvac Inc. are at the top of the list of suppliers selling production-scale OLED deposition equipment. oLED light-emitting materials are generally divided into three categories: small molecules, small molecules, and small molecules, which are used to produce light-emitting materials. OLED light-emitting materials are usually categorized into three types: small molecule materials, polymer materials, and rare-earth light-emitting materials.
At present, small molecule light-emitting materials to Japanese manufacturers as the main supplier (from the U.S. Kodak molecular OLED technology, including Idemitsu Kogyo, Nippon Steel Chemical, Toyo Ink, Toray, etc., accounting for a total of about 80% of the market share); European and American manufacturers to the development of polymer (PLED) materials, the main Covion (has been purchased by the U.S. Me rck), the United Kingdom, the United States, the United States, the United States and Japan’s DuPont and Sumitomo Chemical. Covion (acquired by Me rck), CDT (UK), DuPont (US) and Sumitomo Chemical (Japan).
2 Analysis of OLED Display Industry
Current situation of display industry
According to the different OLED light-emitting materials, the global OLED panel manufacturers can be divided into two camps: small molecule OLED, represented by Kodak, and Sony, Sanyo, TDK, eMagin, Pioneer, Samsung, LG, Rhenium, Univision, Macroview, NEC, and other companies; high molecule OLED including Epson, DuPont, Toshiba and other companies.
Due to the rapid development of small molecule materials, the global mass production of OLED display panels are mainly based on small molecule materials. With the development of AM-OLED technology, in 2007, South Korea’s Samsung SDI invested 500 million U.S. dollars in 2007 to establish a four-generation line of glass substrate size (730mm × 920mm) AMOLED production line, at the same time, LG Electronics also announced a four-generation line of AMOLED production plan. In the second half of 2009, LG released the 15in EL9500 OLED TV, priced at about US$2,500/unit, which will be sold in May 2010 in the European market.
There are more than 20 research institutes and enterprises participating in the R&D and manufacturing of OLED panels in mainland China, including Tsinghua University, South China University of Technology, Jilin University, Shanghai University, Southeast University, Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunication, Hefei University of Technology, Changchun Institute of Optical Mechanics, Institute of Chemistry of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing Visionox, Kunshan Visionox, Sunny Semiconductor, Hongwei Digital of Guangdong Province, Shanghai Radio & Television Electronics Group, and BOE.